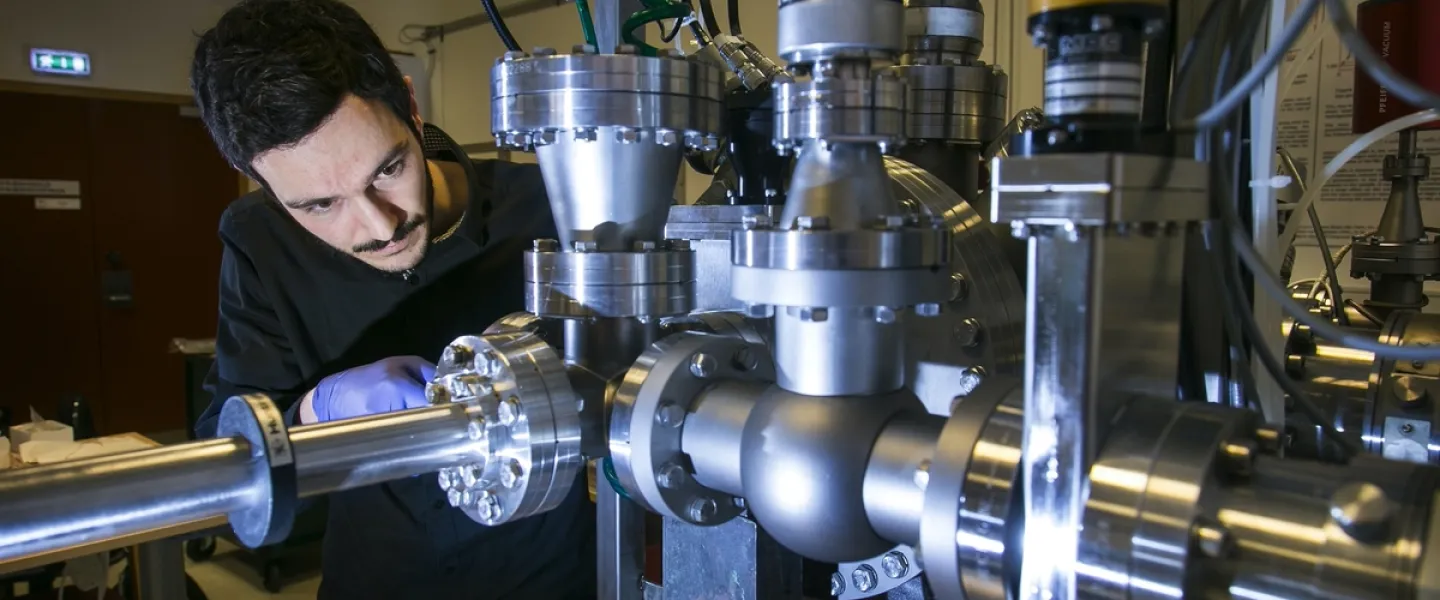
The materials science centre is a core research centre housing instrumentation for advanced materials science and engineering analysis and fabrication. The centre is a collaboration between the University of Iceland, the UI Science Institute, Reykjavik University and IceTec.
The centre coordinates the running and access to advanced research and development infrastructure in Iceland for both academic and industrial research. The centre enables fabrication of materials ranging from additive manufacturing down to microfabrication and detailed material analysis from large scale properties such as hardness and chemical composition down to atomic structure.