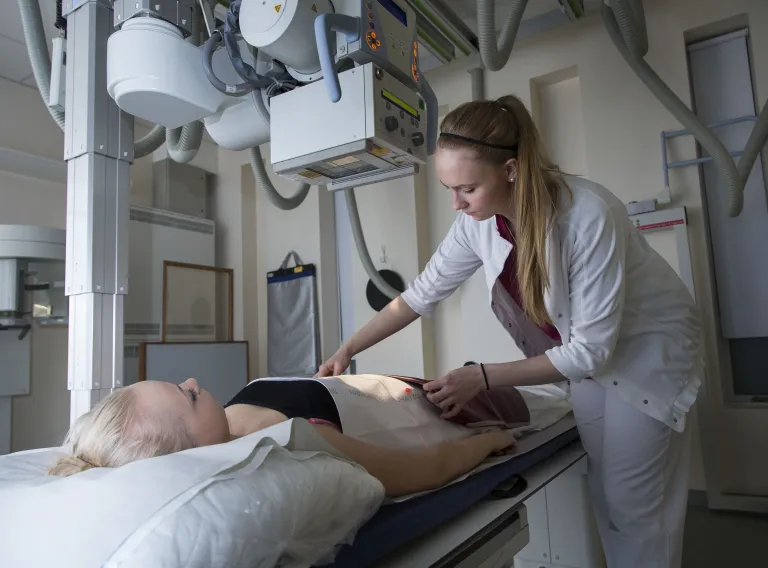

- Are you interested in the human body and how it works?
- Do you want to learn about diseases and how they are diagnosed?
- Do you want to work with patients?
- Are you interested in working with technology and computers?
- Do you want to work in a field that is constantly evolving?
- Do you want to take part in scientific research?
Students will learn about research in different areas of diagnostic imaging, including general X-rays, CT scans, vascular ultrasound and MRI.
You will explore theories involving the methodology and pathology of the main branches of radiography.
Course topics include:
- Physics and chemistry
- Medical imaging and analysis
- Radiation physics
- Research in diagnostic imaging
- Anatomy and physiology
- Patient care
- Radiation protection
- Science and team work, ethics and methodology
- Radiographic equipment
- Microbiology and pharmacology
- CT scans and fluoroscopy
- Magnetic resonance imaging
- Pathology
- Sectional anatomy
- Nuclear medicine
Programme structure
The first year focuses on general knowledge of the human body. Students spend the next two years acquiring specialised knowledge of radiography. Students learn to carry out all the examinations that radiographers are responsible for in Iceland:
- general X-ray imaging
- nuclear medicine
- CT scans
- vascular ultrasound
- MRI scans
A range of teaching and assessment methods are used, including lectures, practical training, independent projects and group work.
The BS programme in radiography, together with an additional 60 ECTS diploma in radiography, confers professional recognition as a radiographer. To qualify as a radiographer therefore takes four years. The diploma programme is also the first year of the Master's programme.
Radiographers provide essential services within the healthcare system. Imaging plays an increasingly vital role in the diagnosis and treatment of a wide range of diseases.
In order to look inside the human body, radiographers use various methods which are under continuous development. Without precise knowledge of what is happening in the body, medical treatments would not be as effective and valuable time would be lost.
Icelandic matriculation examination (stúdentspróf) or a comparative exam from other countries.
A matriculation programme in natural sciences is preferred. Students who complete a matriculation programme in other fields of study are advised to take preparatory classes in physics, chemistry and biology.
Icelandic language proficiency is required as all courses are taught in Icelandic.
180 ECTS must be completed for a bachelor's degree or 60 ECTS per academic year. The programme is structured so that it can be completed in three academic years, and the maximum duration of studies is five years.
All exams for each year must be completed before commencing to the subsequent year of studies.
Programme structure
Check below to see how the programme is structured.
This programme does not offer specialisations.
- First year
- Fall
- Chemistry
- Introduction to medical imaging and analysis
- Radiation Physics 1
- Physics
- Medical imaging 1
- Anatomy
- Cell biology
- Physiology 1
- Spring 1
- Radiation Protection
- Radiation Physics 2
- Medical imaging 2
- Clinical Radiography 1
- Patient care
- Science and data literacy
- Physiology 2
- Introduction to multidisciplinary health sciences - The health science day
Chemistry (GSL101G)
Basic principles of general chemistry, balancing equations, nomenclature, molar calculations, solubility, concentration. Basic principles of quantum chemistry, the atomic structure as a base for chemical properties and their reactions. Electron configuration and formation of chemical bonds. Basic introduction to theories of chemical bonding and molecular geometry and intermolecular forces. Basic principles of organic chemistry, nomenclature of organic compounds and functional groups. Organic polymers.
Teaching and learning activities:
Lectures, problem solving and homework.
Introduction to medical imaging and analysis (GSL102G)
Introduction to the history of medical imaging, from W.C. Röntgen's discoveries to modern technological advancements. The role, activities and obligations of Radiographers in the health care system. Field trips to Radiology Departments.
Radiation Physics 1 (GSL103G)
Introduction to radiation physics, radiation protection and medical imaging. Atoms, photons, electrons, magnetism and electromagnetic radiation, with a focus on x-rays. How x-rays are generated. Gamma radiation, radioactivity and half-life.
Lectures and home assignments based on material from the textbook.
Physics (GSL104G)
Students introduced to the basic applications of physics in health sciences. Example solutions to problems related to forces, motion, energy, etc., which will allow students to pursue further study and work in the health sciences.
Physics: Motion. Forces, Newton's law. Work, energy and power. Degree of heat, heat transport and thermodynamics. Hydrodynamics. Electrical forces and fields. Electricity, voltage and circuit. Magnetic field. Optics.
Lectures and electronic assignments based on the textbook material.
Medical imaging 1 (GSL105G)
Students receive instruction in the research technique used in performing general X-ray studies.
Students learn to view X-rays with respect to proper insertion, the most common variations and major diseases. The major tips and contraindications for X-ray studies will be discussed. The key concepts and word-of-speech radiologists will be discussed.
Students learn the importance of good communication.
Anatomy (LEI102G)
Anatomical methodology and descriptive terms. Terms of orientation with reference to the anatomical position. Fundamental principles of human body structure. Origins of the human body (embryology). Structure and function of the cell. Tissues.
Locomotor system. Nervous system. Cardiovascular system. Respiratory system. Lymphatic system. Digestive system. Urinary system. Endocrine system. Muscular system. Sensory systems. Reproductive system. Immune system. Hormonal system.
Cell biology (LEI107G)
Lectures: Topics, concepts and methods in biochemistry and cell biology. Genetic material, genome and genes, DNA replication and DNA metabolism. RNA, gene expression, transcription and protein translation. Proteins and enzymes. Metabolism of nucleotides, carbohydrates, lipids and amino acids. Nutrition, bioenergetics. Construction and properties of the cell membrane, membrane transport, cell organelles and intracellular transport, cell communication (signaling), the cytoskeleton, cell cycle, cell death and cell division.
Laboratory practicals: Pipettes og measuring techniques, spectrometry in enzymology, isolation of proteins and determination of protein concentration, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), enzyme kinetics.
Physiology 1 (LEI108G)
Lectures: Homeostasis and control systems. Electrophysiology: membrane potentials and conduction. Endocrinology and nervous systems. Sensory physiology. Muscles: skeletal, smooth and cardiac muscles.
Radiation Protection (GSL204G)
The use of radiation in the beginning of the century, radiation injuries. Methods of radiation detection and measurements. Biological effects of radiation on adults, children and foetus. Stochastic and non-stochastic effects of radiation. Carcinogenesis and hereditary effects. The International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP), justification, optimisation and limitation principles. Radiation protection of the workers and patients in diagnostic radiology. Acts and regulations concerning radiation protection. Background radiation, man-made radiation.
Radiation Physics 2 (GSL206G)
Energy spectrum of x-rays and attenuation in matter. Emphasis on how x-rays interact with matter, attenuation coefficients, half-value layers and factors that affect beam attenuation. Scatter radiation, radiation dose, and effective dose. Basic foundation of measurement of ionizing radiation and one practical exercise.
Lectures and a practical exercise related to the lecture material, which will require active participation from students.
Medical imaging 2 (GSL207G)
Students receive instruction in the research technique used in performing general X-ray studies of musculoskeletal, chest and abdominal.
Students learn to view X-rays with respect to proper insertion, the most common variations and major diseases of the musculoskeletal, breast and abdominal conditions. The major tips and contraindications for X-ray studies will be discussed. The key concepts and word-of-speech radiologists will be discussed.
Students learn the importance of good communication.
Clinical Radiography 1 (GSL208G)
The students learn to perform the basics examinations of the skeleton and lungs.
Patient care (GSL209G)
The topic of this course is basic hospital operations and patient care.
Fundamental theories in nursing will be discussed. Students will get an introduction to hospital departments, the characteristics of different specialties, and the activities and roles of healthcare professions.
The course will cover patient admissions, reception, stays, treatment, discharge preparation, and preparation for examinations and operations. Also covered is patient care following operations, complications, and complication prevention.
Students will learn about caring for patients with neurological, metabolic, cardiopulmonary, urological, gastrointestinal, or joint diseases, as well as cancer care. Also nursing care of children and the specific needs of children.
The course will also discuss patient's safety needs and social needs, together with the care of family members. Confidentiality and patients' rights will be introduced, along with correct body posture and work techniques when caring for and transporting patients.
Science and data literacy (LEI205G)
The course is divided into three parts: Presentation of scientific data, Literature search, and scientific and data literacy.
I. Presentation of scientific data
This section covers methodology for professional writing within the health sciences, as well as the structure and delivery of lectures. Database search and reference management software are also addressed. Students apply these methods in course assignments.
II. Literature search
Students receive instruction in the fundamentals of information searching.
III. Scientific and data literacy
An overview of statistics and the origin of data. Graphical representation of data and data distribution types. Confidence intervals. Sensitivity, specificity, and predictive values. An overview of study design and sampling as a representation of a population. Risk factors, risk, and relative risk. Interpretation of research results for an individual. Interpretation of research results in scientific papers and assessment of possible error sources.
The course requires active participation. The material is covered in lectures, while methods are practiced in tutorial sessions and through assignments submitted orally and/or in writing.
Physiology 2 (LEI206G)
Lectures. Cardiovascular-, respiratory-, renal- and gastrointestinal physiology. Energy balance and control of metabolism and physiology of reproduction.
Practical lesson. Cardiovascular system. Participation is obligatory, lab report must be submitted, and online exam taken.
Project lessons. Twice during the course. Participation is obligatory
Partial exams. Three online partial exams will be applied. Students will be informed in more details at the beginning of the course.
Introduction to multidisciplinary health sciences - The health science day (HVS202G)
The course is especially aimed at students on their first year of studies in disciplines within the field of health sciences. The joint Health science day is for incoming students of all faculties at the School of Health Sciences in January each year. The main topic is interdisciplinary cooperation and its importance. All basic factors of cooperation will be covered such as the common view on the right to good health, communication and ethics. Furthermore, the role and responsibility of health sciences.
- Second year
- Fall
- Microbiology and infection control
- Vascular ultrasound
- Clinical Radiography 2
- Radiographic Equipment
- Ethics
- CPR
- Pharmacology and Contrast Media
- Spring 1
- MRI Magnetic Resonance Imaging 1
- CT technology 1
- Clinical Radiography 3
- Sectional anatomy
- Fluoroscopy
- Medical imaging 3
Microbiology and infection control (GSL302G)
The course consists of two main parts, microbiology and infection control. These parts are intergraded and provide the basis for knowledge and understanding of the characteristics of different pathogens and their relations to infectious diseases and the methods you can use for prevention of nosocomial or healthcare-associated infections.
Teaching/learning procedures:
In the teaching is based on lectures and includes following parts:
- Microbiology – basics
- Microbiology – species/groups
- Bacterial infections in diverse organs and organ systems and major species in healthcare associated infections.
- Infection control
Vascular ultrasound (GSL307G)
This course will cover the basics of ultrasound imaging such as physics of sound waves, properties of reflection from major tissues and main processing methods and their use. Also, the functionality of the ultrasound equipment will be introduced in detail along with discussion of the importance of image quality, its improvement and impact factors.
Carotid artery is the main subject with introduction to cardiovascular ultrasound. The anatomy of the carotid artery along with the surrounding tissues and their appearance in ultrasound images will be described. Students learn to recognize and identify the normal appearance of the carotid artery in ultrasound images and also identify and recognize common abnormalities and major manifestations. Students are given tasks where they perform ultrasound imaging of the common carotid artery and process their results.
Clinical Radiography 2 (GSL309G)
Students receive training in performing general X-ray examinations. Receive training in contrast material handling and needle placement. Receive training in performing simple CT scans.
Radiographic Equipment (GSL310G)
General introduction of common radiographic equipment and short overview of the history of radiographic imaging. Introduction of equipment for mammography, tomography, dental radiography and veterinary use.
Basic properties of digital images. Pixels, their size and depth; monochrome and color images, greyscale and different color models. Image file formats and compression. Contrast- and spatial resolution. Fundamentals of digital image processing: look-up-tables and spatial filtering. Image quality and visual perception.
Quality, quantity and geometry of an x-ray beam; effect on image quality. The primary X-ray image. Scatter grids and compensation filters. Appropriate exposure; timers and automatic exposure control, exposure indices, exposure factors and charts.
Digital image receptors; flat panel detectors and computed radiography. Basic construction, function, sensitivity and resolution. Image artefacts and the effects of image processing on image quality.
Students are required to participate in group work and practical exercises.
Ethics (GSL311G)
The course aims to strengthen students' independent thinking. We will discuss how best to discuss ethical problems and analyze ethical arguments. Common theories in ethics will also be discussed critically. Awareness of the principles underlying human relations and behaviours will be covered as well as the Code of Ethics for Radiologists.
CPR (GSL313G)
First aid training.
Pharmacology and Contrast Media (GSL314G)
History and development of CM.
Classification of CM.
Chemistry of CM.
Effects on CM on various body systems.
Indications and contraindication.
Patient risk groups and possible adverse reactions.
Acute and allergic reactions.
Pharmacology and drug effects.
MRI Magnetic Resonance Imaging 1 (GSL401G)
The structure and major components of magnetic resonance imaging equipment. Fundamental mathematics and physics of MRI. Magnetization of the body, the fundamentals of imaging and image reconstruction in MRI. MRI hardware and how individual components work. Overview of pulse sequences, rapid imaging, image quality and image artifacts. Pulse sequence for angiography and the use of contrast agents. Investigations of different parts of the body, patient preparation and patient care. Diseases seen in MRI. MRI safety.
CT technology 1 (GSL411G)
Basic principles of computed tomography (CT), from x-ray beam attenuation to radiation detection, image reconstruction and display. The main factors affecting quality of CT examinations, in data acquisition as well as image reconstruction. Processing and visualization of images. CT examination procedures, contrast media, positioning and parameter selection.
Clinical Radiography 3 (GSL412G)
Students are trained in radiographic positioning and procedures. Emphasis is placed on performing CT examinations, pediatric radiography and fluoroscopy.
Sectional anatomy (GSL413G)
• Students are introduced to sectional anatomical plans - The appearance and characteristics of organs and organ systems in cross-section and other plans are discussed.
• Students are introduced to sectional anatomy and where they can look to review and gain more knowledge.
• The sectional anatomy will be reviewed as follows: sectional plans and review of bones, abdomen, thorax, spine, head and limbs.
• The course is mostly self-study with continuous assessment.
Fluoroscopy (GSL414G)
Fluoroscopy and intervention: Equipment, techniques and radiation protection of patients and workers.
Equipment for measuring radiation dose and different methods for estimating effective dose.
Variation in effective doses and diagnostic reference levels.
Students are required to participate in group work and practical exercises.
Medical imaging 3 (GSL415G)
In all imaging departments, radiographers carry out medical imaging examinations and interventional procedures. It is important that radiologists, who carry out research, practice professional practices and show respect and devotion to their clients.
The aim of the course is to teach students to look at X-ray images while considering the correct projection, the most common abnormalities and the main diseases. Students are taught settings and how to see faults in projection and correct them.
Students learn about accident and emergency imaging performed outside of imaging departments. Students learn about the importance of professional and good communication with patients and colleagues.
- Third year
- Fall
- Pediatric X-ray
- Magnetic Resonance Imagin 2
- Clinical Radiography 4
- Nuclear medicine 1
- Scientific Research methods
- Spring 1
- Pathology
- Clinical radiography 5
- CT technology 2
- BS Project in Radiography
Pediatric X-ray (GSL503G)
Pediatric imaging is an important part of the work of radiographers. In all imaging departments, children are part of the clients who come to the department and it is important that radiographers who perform imaging studies on children practice professional work practices and show children respect and care.
The aim of the course is to introduce students to pediatric imaging and the importance of good preparation for the radiographer when receiving children and their families.
The course will cover, among other things, the main pediatric diseases and injuries in children. The preparation, performance, lead protection and radiation protection of the main imaging studies will be reviewed. We will emphasize general X-ray studies but also introduce students to other imaging studies such as computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), ultrasound and isotopes.
Magnetic Resonance Imagin 2 (GSL505G)
MRI course, part II: The aim of the course is to enhance the students knowledge of the basic physics of MRI introduced in part I of the MRI course (previous semester) and to associate the physics of MRI to clinical applications. The course consists of the following items:
- Pulse sequences and image contrast
- Tissue relaxation properties together with tissue proton density and appearance on images
- Historical developments in clinical MRI applications
- Examinations of organs and body-systems based on applications, indications, pathology and diagnosis. Includes central nervous system, muscular-skeletal system, thorax, heart and vasculature.
- Contrast agents in MRI: Types, indications for use and applications
- MRI safety
Clinical Radiography 4 (GSL508G)
Execute general radiography examination. Emphasis is on training in angiography and MRI examination and procedures.
Nuclear medicine 1 (GSL509G)
Radioactivity, handling of radioactive material, examinations and imaging with gamma rays.
Radioactivity, alpha, beta and gamma radiation, decay and half-life.
An overview of production, transport, inventory and disposal of radioactive materials. Laws and regulations, with an emphasis on open radiation sources. Radionuclide generators, facilities, work practices and radiation protection. Handling, radiopharmacy and quality control of isotopes and carriers. Imaging with a gamma camera.
Diagnostic imaging with technetium, and other gamma-emitting substances, of the digestive system, urinary system, musculoskeletal system, respiratory system, endocrine system, cardiovascular system, and nervous system.
Scientific Research methods (GSL510G)
The course constitutes a practical guide to the preparation of a health-related research study. Modules include: reference search and handling, development of hypotheses, creation of a systematic critical review within chosen field of research, development and presentation of research proposals.
The course provide students knowledge of useful statistical methods appropriate for their project. The student also prepare and apply for a license according to their research.
The course is for graduate students who have chosen a field/research question for their dissertation project.
Pathology (GSL611G)
This course aims for the student to gain an overview of the main diseases in the following categories: Cardiology, orthopedics (injuries and cold orthopedia), lung diseases, gastroenterology, neptrology, infectionous diseases, endocrine and metabolic diseases, brain and nervous diseases. Psychiatric and ear and throat. Normal appearance in X-ray, deviation, indications and contraindications. Diagnostic imaging.
Clinical radiography 5 (GSL612G)
Clinical training in medical imaging department. Training in general radiographic examinations procedures. Emphasis is on nuclear medicine and MRI examinations.
CT technology 2 (GSL613G)
Clinical use of CT, indications and pathology in which CT examinations are most useful. Basic examinations of head, neck, spine, abdomen, and thorax. Radiation protection of patient and personnel related to CT examinations, radiation dose measurements and estimation of effective doses. Specific consideration for children and pregnant women.
The role of CT in nuclear medicine, CT angiographies and intervention.
BS Project in Radiography (GSL614L)
Students select their own field of study in radiography and supply their knowledge in the field. Students work on a final paper according to their interest under supervision and present the results.
- Fall
- GSL101GChemistryMandatory (required) course4A mandatory (required) course for the programme4 ECTS, creditsCourse Description
Basic principles of general chemistry, balancing equations, nomenclature, molar calculations, solubility, concentration. Basic principles of quantum chemistry, the atomic structure as a base for chemical properties and their reactions. Electron configuration and formation of chemical bonds. Basic introduction to theories of chemical bonding and molecular geometry and intermolecular forces. Basic principles of organic chemistry, nomenclature of organic compounds and functional groups. Organic polymers.
Teaching and learning activities:
Lectures, problem solving and homework.Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL102GIntroduction to medical imaging and analysisMandatory (required) course0A mandatory (required) course for the programme0 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionIntroduction to the history of medical imaging, from W.C. Röntgen's discoveries to modern technological advancements. The role, activities and obligations of Radiographers in the health care system. Field trips to Radiology Departments.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL103GRadiation Physics 1Mandatory (required) course4A mandatory (required) course for the programme4 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionIntroduction to radiation physics, radiation protection and medical imaging. Atoms, photons, electrons, magnetism and electromagnetic radiation, with a focus on x-rays. How x-rays are generated. Gamma radiation, radioactivity and half-life.
Lectures and home assignments based on material from the textbook.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL104GPhysicsMandatory (required) course2A mandatory (required) course for the programme2 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionStudents introduced to the basic applications of physics in health sciences. Example solutions to problems related to forces, motion, energy, etc., which will allow students to pursue further study and work in the health sciences.
Physics: Motion. Forces, Newton's law. Work, energy and power. Degree of heat, heat transport and thermodynamics. Hydrodynamics. Electrical forces and fields. Electricity, voltage and circuit. Magnetic field. Optics.
Lectures and electronic assignments based on the textbook material.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL105GMedical imaging 1Mandatory (required) course4A mandatory (required) course for the programme4 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionStudents receive instruction in the research technique used in performing general X-ray studies.
Students learn to view X-rays with respect to proper insertion, the most common variations and major diseases. The major tips and contraindications for X-ray studies will be discussed. The key concepts and word-of-speech radiologists will be discussed.
Students learn the importance of good communication.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesLEI102GAnatomyMandatory (required) course8A mandatory (required) course for the programme8 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionAnatomical methodology and descriptive terms. Terms of orientation with reference to the anatomical position. Fundamental principles of human body structure. Origins of the human body (embryology). Structure and function of the cell. Tissues.
Locomotor system. Nervous system. Cardiovascular system. Respiratory system. Lymphatic system. Digestive system. Urinary system. Endocrine system. Muscular system. Sensory systems. Reproductive system. Immune system. Hormonal system.Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesLEI107GCell biologyMandatory (required) course4A mandatory (required) course for the programme4 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionLectures: Topics, concepts and methods in biochemistry and cell biology. Genetic material, genome and genes, DNA replication and DNA metabolism. RNA, gene expression, transcription and protein translation. Proteins and enzymes. Metabolism of nucleotides, carbohydrates, lipids and amino acids. Nutrition, bioenergetics. Construction and properties of the cell membrane, membrane transport, cell organelles and intracellular transport, cell communication (signaling), the cytoskeleton, cell cycle, cell death and cell division.
Laboratory practicals: Pipettes og measuring techniques, spectrometry in enzymology, isolation of proteins and determination of protein concentration, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), enzyme kinetics.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesAttendance required in classLEI108GPhysiology 1Mandatory (required) course4A mandatory (required) course for the programme4 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionLectures: Homeostasis and control systems. Electrophysiology: membrane potentials and conduction. Endocrinology and nervous systems. Sensory physiology. Muscles: skeletal, smooth and cardiac muscles.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisites- Spring 2
GSL204GRadiation ProtectionMandatory (required) course4A mandatory (required) course for the programme4 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionThe use of radiation in the beginning of the century, radiation injuries. Methods of radiation detection and measurements. Biological effects of radiation on adults, children and foetus. Stochastic and non-stochastic effects of radiation. Carcinogenesis and hereditary effects. The International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP), justification, optimisation and limitation principles. Radiation protection of the workers and patients in diagnostic radiology. Acts and regulations concerning radiation protection. Background radiation, man-made radiation.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL206GRadiation Physics 2Mandatory (required) course4A mandatory (required) course for the programme4 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionEnergy spectrum of x-rays and attenuation in matter. Emphasis on how x-rays interact with matter, attenuation coefficients, half-value layers and factors that affect beam attenuation. Scatter radiation, radiation dose, and effective dose. Basic foundation of measurement of ionizing radiation and one practical exercise.
Lectures and a practical exercise related to the lecture material, which will require active participation from students.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL207GMedical imaging 2Mandatory (required) course3A mandatory (required) course for the programme3 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionStudents receive instruction in the research technique used in performing general X-ray studies of musculoskeletal, chest and abdominal.
Students learn to view X-rays with respect to proper insertion, the most common variations and major diseases of the musculoskeletal, breast and abdominal conditions. The major tips and contraindications for X-ray studies will be discussed. The key concepts and word-of-speech radiologists will be discussed.
Students learn the importance of good communication.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL208GClinical Radiography 1Mandatory (required) course5A mandatory (required) course for the programme5 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionThe students learn to perform the basics examinations of the skeleton and lungs.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesAttendance required in classGSL209GPatient careMandatory (required) course4A mandatory (required) course for the programme4 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionThe topic of this course is basic hospital operations and patient care.
Fundamental theories in nursing will be discussed. Students will get an introduction to hospital departments, the characteristics of different specialties, and the activities and roles of healthcare professions.
The course will cover patient admissions, reception, stays, treatment, discharge preparation, and preparation for examinations and operations. Also covered is patient care following operations, complications, and complication prevention.
Students will learn about caring for patients with neurological, metabolic, cardiopulmonary, urological, gastrointestinal, or joint diseases, as well as cancer care. Also nursing care of children and the specific needs of children.
The course will also discuss patient's safety needs and social needs, together with the care of family members. Confidentiality and patients' rights will be introduced, along with correct body posture and work techniques when caring for and transporting patients.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesLEI205GScience and data literacyMandatory (required) course6A mandatory (required) course for the programme6 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionThe course is divided into three parts: Presentation of scientific data, Literature search, and scientific and data literacy.
I. Presentation of scientific data
This section covers methodology for professional writing within the health sciences, as well as the structure and delivery of lectures. Database search and reference management software are also addressed. Students apply these methods in course assignments.
II. Literature search
Students receive instruction in the fundamentals of information searching.
III. Scientific and data literacy
An overview of statistics and the origin of data. Graphical representation of data and data distribution types. Confidence intervals. Sensitivity, specificity, and predictive values. An overview of study design and sampling as a representation of a population. Risk factors, risk, and relative risk. Interpretation of research results for an individual. Interpretation of research results in scientific papers and assessment of possible error sources.The course requires active participation. The material is covered in lectures, while methods are practiced in tutorial sessions and through assignments submitted orally and/or in writing.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesLEI206GPhysiology 2Mandatory (required) course4A mandatory (required) course for the programme4 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionLectures. Cardiovascular-, respiratory-, renal- and gastrointestinal physiology. Energy balance and control of metabolism and physiology of reproduction.
Practical lesson. Cardiovascular system. Participation is obligatory, lab report must be submitted, and online exam taken.
Project lessons. Twice during the course. Participation is obligatory
Partial exams. Three online partial exams will be applied. Students will be informed in more details at the beginning of the course.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesExtra material fee collectedHVS202GIntroduction to multidisciplinary health sciences - The health science dayMandatory (required) course1A mandatory (required) course for the programme1 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionThe course is especially aimed at students on their first year of studies in disciplines within the field of health sciences. The joint Health science day is for incoming students of all faculties at the School of Health Sciences in January each year. The main topic is interdisciplinary cooperation and its importance. All basic factors of cooperation will be covered such as the common view on the right to good health, communication and ethics. Furthermore, the role and responsibility of health sciences.
Distance learningPrerequisitesAttendance required in class- Fall
- GSL302GMicrobiology and infection controlMandatory (required) course4A mandatory (required) course for the programme4 ECTS, creditsCourse Description
The course consists of two main parts, microbiology and infection control. These parts are intergraded and provide the basis for knowledge and understanding of the characteristics of different pathogens and their relations to infectious diseases and the methods you can use for prevention of nosocomial or healthcare-associated infections.
Teaching/learning procedures:
In the teaching is based on lectures and includes following parts:- Microbiology – basics
- Microbiology – species/groups
- Bacterial infections in diverse organs and organ systems and major species in healthcare associated infections.
- Infection control
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL307GVascular ultrasoundMandatory (required) course4A mandatory (required) course for the programme4 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionThis course will cover the basics of ultrasound imaging such as physics of sound waves, properties of reflection from major tissues and main processing methods and their use. Also, the functionality of the ultrasound equipment will be introduced in detail along with discussion of the importance of image quality, its improvement and impact factors.
Carotid artery is the main subject with introduction to cardiovascular ultrasound. The anatomy of the carotid artery along with the surrounding tissues and their appearance in ultrasound images will be described. Students learn to recognize and identify the normal appearance of the carotid artery in ultrasound images and also identify and recognize common abnormalities and major manifestations. Students are given tasks where they perform ultrasound imaging of the common carotid artery and process their results.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL309GClinical Radiography 2Mandatory (required) course8A mandatory (required) course for the programme8 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionStudents receive training in performing general X-ray examinations. Receive training in contrast material handling and needle placement. Receive training in performing simple CT scans.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesAttendance required in classGSL310GRadiographic EquipmentMandatory (required) course6A mandatory (required) course for the programme6 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionGeneral introduction of common radiographic equipment and short overview of the history of radiographic imaging. Introduction of equipment for mammography, tomography, dental radiography and veterinary use.
Basic properties of digital images. Pixels, their size and depth; monochrome and color images, greyscale and different color models. Image file formats and compression. Contrast- and spatial resolution. Fundamentals of digital image processing: look-up-tables and spatial filtering. Image quality and visual perception.
Quality, quantity and geometry of an x-ray beam; effect on image quality. The primary X-ray image. Scatter grids and compensation filters. Appropriate exposure; timers and automatic exposure control, exposure indices, exposure factors and charts.
Digital image receptors; flat panel detectors and computed radiography. Basic construction, function, sensitivity and resolution. Image artefacts and the effects of image processing on image quality.
Students are required to participate in group work and practical exercises.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL311GEthicsMandatory (required) course2A mandatory (required) course for the programme2 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionThe course aims to strengthen students' independent thinking. We will discuss how best to discuss ethical problems and analyze ethical arguments. Common theories in ethics will also be discussed critically. Awareness of the principles underlying human relations and behaviours will be covered as well as the Code of Ethics for Radiologists.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL313GCPRMandatory (required) course1A mandatory (required) course for the programme1 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionFirst aid training.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL314GPharmacology and Contrast MediaMandatory (required) course5A mandatory (required) course for the programme5 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionHistory and development of CM.
Classification of CM.
Chemistry of CM.
Effects on CM on various body systems.
Indications and contraindication.
Patient risk groups and possible adverse reactions.
Acute and allergic reactions.
Pharmacology and drug effects.Face-to-face learningPrerequisites- Spring 2
GSL401GMRI Magnetic Resonance Imaging 1Mandatory (required) course6A mandatory (required) course for the programme6 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionThe structure and major components of magnetic resonance imaging equipment. Fundamental mathematics and physics of MRI. Magnetization of the body, the fundamentals of imaging and image reconstruction in MRI. MRI hardware and how individual components work. Overview of pulse sequences, rapid imaging, image quality and image artifacts. Pulse sequence for angiography and the use of contrast agents. Investigations of different parts of the body, patient preparation and patient care. Diseases seen in MRI. MRI safety.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesAttendance required in classGSL411GCT technology 1Mandatory (required) course4A mandatory (required) course for the programme4 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionBasic principles of computed tomography (CT), from x-ray beam attenuation to radiation detection, image reconstruction and display. The main factors affecting quality of CT examinations, in data acquisition as well as image reconstruction. Processing and visualization of images. CT examination procedures, contrast media, positioning and parameter selection.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL412GClinical Radiography 3Mandatory (required) course10A mandatory (required) course for the programme10 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionStudents are trained in radiographic positioning and procedures. Emphasis is placed on performing CT examinations, pediatric radiography and fluoroscopy.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesAttendance required in classGSL413GSectional anatomyMandatory (required) course2A mandatory (required) course for the programme2 ECTS, creditsCourse Description• Students are introduced to sectional anatomical plans - The appearance and characteristics of organs and organ systems in cross-section and other plans are discussed.
• Students are introduced to sectional anatomy and where they can look to review and gain more knowledge.
• The sectional anatomy will be reviewed as follows: sectional plans and review of bones, abdomen, thorax, spine, head and limbs.
• The course is mostly self-study with continuous assessment.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL414GFluoroscopyMandatory (required) course4A mandatory (required) course for the programme4 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionFluoroscopy and intervention: Equipment, techniques and radiation protection of patients and workers.
Equipment for measuring radiation dose and different methods for estimating effective dose.
Variation in effective doses and diagnostic reference levels.
Students are required to participate in group work and practical exercises.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL415GMedical imaging 3Mandatory (required) course4A mandatory (required) course for the programme4 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionIn all imaging departments, radiographers carry out medical imaging examinations and interventional procedures. It is important that radiologists, who carry out research, practice professional practices and show respect and devotion to their clients.
The aim of the course is to teach students to look at X-ray images while considering the correct projection, the most common abnormalities and the main diseases. Students are taught settings and how to see faults in projection and correct them.
Students learn about accident and emergency imaging performed outside of imaging departments. Students learn about the importance of professional and good communication with patients and colleagues.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisites- Fall
- GSL503GPediatric X-rayMandatory (required) course6A mandatory (required) course for the programme6 ECTS, creditsCourse Description
Pediatric imaging is an important part of the work of radiographers. In all imaging departments, children are part of the clients who come to the department and it is important that radiographers who perform imaging studies on children practice professional work practices and show children respect and care.
The aim of the course is to introduce students to pediatric imaging and the importance of good preparation for the radiographer when receiving children and their families.
The course will cover, among other things, the main pediatric diseases and injuries in children. The preparation, performance, lead protection and radiation protection of the main imaging studies will be reviewed. We will emphasize general X-ray studies but also introduce students to other imaging studies such as computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), ultrasound and isotopes.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL505GMagnetic Resonance Imagin 2Mandatory (required) course6A mandatory (required) course for the programme6 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionMRI course, part II: The aim of the course is to enhance the students knowledge of the basic physics of MRI introduced in part I of the MRI course (previous semester) and to associate the physics of MRI to clinical applications. The course consists of the following items:
- Pulse sequences and image contrast
- Tissue relaxation properties together with tissue proton density and appearance on images
- Historical developments in clinical MRI applications
- Examinations of organs and body-systems based on applications, indications, pathology and diagnosis. Includes central nervous system, muscular-skeletal system, thorax, heart and vasculature.
- Contrast agents in MRI: Types, indications for use and applications
- MRI safety
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL508GClinical Radiography 4Mandatory (required) course9A mandatory (required) course for the programme9 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionExecute general radiography examination. Emphasis is on training in angiography and MRI examination and procedures.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesAttendance required in classGSL509GNuclear medicine 1Mandatory (required) course4A mandatory (required) course for the programme4 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionRadioactivity, handling of radioactive material, examinations and imaging with gamma rays.
Radioactivity, alpha, beta and gamma radiation, decay and half-life.
An overview of production, transport, inventory and disposal of radioactive materials. Laws and regulations, with an emphasis on open radiation sources. Radionuclide generators, facilities, work practices and radiation protection. Handling, radiopharmacy and quality control of isotopes and carriers. Imaging with a gamma camera.
Diagnostic imaging with technetium, and other gamma-emitting substances, of the digestive system, urinary system, musculoskeletal system, respiratory system, endocrine system, cardiovascular system, and nervous system.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL510GScientific Research methodsMandatory (required) course5A mandatory (required) course for the programme5 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionThe course constitutes a practical guide to the preparation of a health-related research study. Modules include: reference search and handling, development of hypotheses, creation of a systematic critical review within chosen field of research, development and presentation of research proposals.
The course provide students knowledge of useful statistical methods appropriate for their project. The student also prepare and apply for a license according to their research.
The course is for graduate students who have chosen a field/research question for their dissertation project.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisites- Spring 2
GSL611GPathologyMandatory (required) course6A mandatory (required) course for the programme6 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionThis course aims for the student to gain an overview of the main diseases in the following categories: Cardiology, orthopedics (injuries and cold orthopedia), lung diseases, gastroenterology, neptrology, infectionous diseases, endocrine and metabolic diseases, brain and nervous diseases. Psychiatric and ear and throat. Normal appearance in X-ray, deviation, indications and contraindications. Diagnostic imaging.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL612GClinical radiography 5Mandatory (required) course5A mandatory (required) course for the programme5 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionClinical training in medical imaging department. Training in general radiographic examinations procedures. Emphasis is on nuclear medicine and MRI examinations.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesAttendance required in classGSL613GCT technology 2Mandatory (required) course4A mandatory (required) course for the programme4 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionClinical use of CT, indications and pathology in which CT examinations are most useful. Basic examinations of head, neck, spine, abdomen, and thorax. Radiation protection of patient and personnel related to CT examinations, radiation dose measurements and estimation of effective doses. Specific consideration for children and pregnant women.
The role of CT in nuclear medicine, CT angiographies and intervention.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL614LBS Project in RadiographyMandatory (required) course30A mandatory (required) course for the programme30 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionStudents select their own field of study in radiography and supply their knowledge in the field. Students work on a final paper according to their interest under supervision and present the results.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesPart of the total project/thesis creditsSecond year- Fall
- GSL101GChemistryMandatory (required) course4A mandatory (required) course for the programme4 ECTS, creditsCourse Description
Basic principles of general chemistry, balancing equations, nomenclature, molar calculations, solubility, concentration. Basic principles of quantum chemistry, the atomic structure as a base for chemical properties and their reactions. Electron configuration and formation of chemical bonds. Basic introduction to theories of chemical bonding and molecular geometry and intermolecular forces. Basic principles of organic chemistry, nomenclature of organic compounds and functional groups. Organic polymers.
Teaching and learning activities:
Lectures, problem solving and homework.Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL102GIntroduction to medical imaging and analysisMandatory (required) course0A mandatory (required) course for the programme0 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionIntroduction to the history of medical imaging, from W.C. Röntgen's discoveries to modern technological advancements. The role, activities and obligations of Radiographers in the health care system. Field trips to Radiology Departments.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL103GRadiation Physics 1Mandatory (required) course4A mandatory (required) course for the programme4 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionIntroduction to radiation physics, radiation protection and medical imaging. Atoms, photons, electrons, magnetism and electromagnetic radiation, with a focus on x-rays. How x-rays are generated. Gamma radiation, radioactivity and half-life.
Lectures and home assignments based on material from the textbook.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL104GPhysicsMandatory (required) course2A mandatory (required) course for the programme2 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionStudents introduced to the basic applications of physics in health sciences. Example solutions to problems related to forces, motion, energy, etc., which will allow students to pursue further study and work in the health sciences.
Physics: Motion. Forces, Newton's law. Work, energy and power. Degree of heat, heat transport and thermodynamics. Hydrodynamics. Electrical forces and fields. Electricity, voltage and circuit. Magnetic field. Optics.
Lectures and electronic assignments based on the textbook material.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL105GMedical imaging 1Mandatory (required) course4A mandatory (required) course for the programme4 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionStudents receive instruction in the research technique used in performing general X-ray studies.
Students learn to view X-rays with respect to proper insertion, the most common variations and major diseases. The major tips and contraindications for X-ray studies will be discussed. The key concepts and word-of-speech radiologists will be discussed.
Students learn the importance of good communication.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesLEI102GAnatomyMandatory (required) course8A mandatory (required) course for the programme8 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionAnatomical methodology and descriptive terms. Terms of orientation with reference to the anatomical position. Fundamental principles of human body structure. Origins of the human body (embryology). Structure and function of the cell. Tissues.
Locomotor system. Nervous system. Cardiovascular system. Respiratory system. Lymphatic system. Digestive system. Urinary system. Endocrine system. Muscular system. Sensory systems. Reproductive system. Immune system. Hormonal system.Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesLEI107GCell biologyMandatory (required) course4A mandatory (required) course for the programme4 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionLectures: Topics, concepts and methods in biochemistry and cell biology. Genetic material, genome and genes, DNA replication and DNA metabolism. RNA, gene expression, transcription and protein translation. Proteins and enzymes. Metabolism of nucleotides, carbohydrates, lipids and amino acids. Nutrition, bioenergetics. Construction and properties of the cell membrane, membrane transport, cell organelles and intracellular transport, cell communication (signaling), the cytoskeleton, cell cycle, cell death and cell division.
Laboratory practicals: Pipettes og measuring techniques, spectrometry in enzymology, isolation of proteins and determination of protein concentration, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), enzyme kinetics.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesAttendance required in classLEI108GPhysiology 1Mandatory (required) course4A mandatory (required) course for the programme4 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionLectures: Homeostasis and control systems. Electrophysiology: membrane potentials and conduction. Endocrinology and nervous systems. Sensory physiology. Muscles: skeletal, smooth and cardiac muscles.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisites- Spring 2
GSL204GRadiation ProtectionMandatory (required) course4A mandatory (required) course for the programme4 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionThe use of radiation in the beginning of the century, radiation injuries. Methods of radiation detection and measurements. Biological effects of radiation on adults, children and foetus. Stochastic and non-stochastic effects of radiation. Carcinogenesis and hereditary effects. The International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP), justification, optimisation and limitation principles. Radiation protection of the workers and patients in diagnostic radiology. Acts and regulations concerning radiation protection. Background radiation, man-made radiation.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL206GRadiation Physics 2Mandatory (required) course4A mandatory (required) course for the programme4 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionEnergy spectrum of x-rays and attenuation in matter. Emphasis on how x-rays interact with matter, attenuation coefficients, half-value layers and factors that affect beam attenuation. Scatter radiation, radiation dose, and effective dose. Basic foundation of measurement of ionizing radiation and one practical exercise.
Lectures and a practical exercise related to the lecture material, which will require active participation from students.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL207GMedical imaging 2Mandatory (required) course3A mandatory (required) course for the programme3 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionStudents receive instruction in the research technique used in performing general X-ray studies of musculoskeletal, chest and abdominal.
Students learn to view X-rays with respect to proper insertion, the most common variations and major diseases of the musculoskeletal, breast and abdominal conditions. The major tips and contraindications for X-ray studies will be discussed. The key concepts and word-of-speech radiologists will be discussed.
Students learn the importance of good communication.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL208GClinical Radiography 1Mandatory (required) course5A mandatory (required) course for the programme5 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionThe students learn to perform the basics examinations of the skeleton and lungs.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesAttendance required in classGSL209GPatient careMandatory (required) course4A mandatory (required) course for the programme4 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionThe topic of this course is basic hospital operations and patient care.
Fundamental theories in nursing will be discussed. Students will get an introduction to hospital departments, the characteristics of different specialties, and the activities and roles of healthcare professions.
The course will cover patient admissions, reception, stays, treatment, discharge preparation, and preparation for examinations and operations. Also covered is patient care following operations, complications, and complication prevention.
Students will learn about caring for patients with neurological, metabolic, cardiopulmonary, urological, gastrointestinal, or joint diseases, as well as cancer care. Also nursing care of children and the specific needs of children.
The course will also discuss patient's safety needs and social needs, together with the care of family members. Confidentiality and patients' rights will be introduced, along with correct body posture and work techniques when caring for and transporting patients.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesLEI205GScience and data literacyMandatory (required) course6A mandatory (required) course for the programme6 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionThe course is divided into three parts: Presentation of scientific data, Literature search, and scientific and data literacy.
I. Presentation of scientific data
This section covers methodology for professional writing within the health sciences, as well as the structure and delivery of lectures. Database search and reference management software are also addressed. Students apply these methods in course assignments.
II. Literature search
Students receive instruction in the fundamentals of information searching.
III. Scientific and data literacy
An overview of statistics and the origin of data. Graphical representation of data and data distribution types. Confidence intervals. Sensitivity, specificity, and predictive values. An overview of study design and sampling as a representation of a population. Risk factors, risk, and relative risk. Interpretation of research results for an individual. Interpretation of research results in scientific papers and assessment of possible error sources.The course requires active participation. The material is covered in lectures, while methods are practiced in tutorial sessions and through assignments submitted orally and/or in writing.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesLEI206GPhysiology 2Mandatory (required) course4A mandatory (required) course for the programme4 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionLectures. Cardiovascular-, respiratory-, renal- and gastrointestinal physiology. Energy balance and control of metabolism and physiology of reproduction.
Practical lesson. Cardiovascular system. Participation is obligatory, lab report must be submitted, and online exam taken.
Project lessons. Twice during the course. Participation is obligatory
Partial exams. Three online partial exams will be applied. Students will be informed in more details at the beginning of the course.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesExtra material fee collectedHVS202GIntroduction to multidisciplinary health sciences - The health science dayMandatory (required) course1A mandatory (required) course for the programme1 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionThe course is especially aimed at students on their first year of studies in disciplines within the field of health sciences. The joint Health science day is for incoming students of all faculties at the School of Health Sciences in January each year. The main topic is interdisciplinary cooperation and its importance. All basic factors of cooperation will be covered such as the common view on the right to good health, communication and ethics. Furthermore, the role and responsibility of health sciences.
Distance learningPrerequisitesAttendance required in class- Fall
- GSL302GMicrobiology and infection controlMandatory (required) course4A mandatory (required) course for the programme4 ECTS, creditsCourse Description
The course consists of two main parts, microbiology and infection control. These parts are intergraded and provide the basis for knowledge and understanding of the characteristics of different pathogens and their relations to infectious diseases and the methods you can use for prevention of nosocomial or healthcare-associated infections.
Teaching/learning procedures:
In the teaching is based on lectures and includes following parts:- Microbiology – basics
- Microbiology – species/groups
- Bacterial infections in diverse organs and organ systems and major species in healthcare associated infections.
- Infection control
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL307GVascular ultrasoundMandatory (required) course4A mandatory (required) course for the programme4 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionThis course will cover the basics of ultrasound imaging such as physics of sound waves, properties of reflection from major tissues and main processing methods and their use. Also, the functionality of the ultrasound equipment will be introduced in detail along with discussion of the importance of image quality, its improvement and impact factors.
Carotid artery is the main subject with introduction to cardiovascular ultrasound. The anatomy of the carotid artery along with the surrounding tissues and their appearance in ultrasound images will be described. Students learn to recognize and identify the normal appearance of the carotid artery in ultrasound images and also identify and recognize common abnormalities and major manifestations. Students are given tasks where they perform ultrasound imaging of the common carotid artery and process their results.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL309GClinical Radiography 2Mandatory (required) course8A mandatory (required) course for the programme8 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionStudents receive training in performing general X-ray examinations. Receive training in contrast material handling and needle placement. Receive training in performing simple CT scans.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesAttendance required in classGSL310GRadiographic EquipmentMandatory (required) course6A mandatory (required) course for the programme6 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionGeneral introduction of common radiographic equipment and short overview of the history of radiographic imaging. Introduction of equipment for mammography, tomography, dental radiography and veterinary use.
Basic properties of digital images. Pixels, their size and depth; monochrome and color images, greyscale and different color models. Image file formats and compression. Contrast- and spatial resolution. Fundamentals of digital image processing: look-up-tables and spatial filtering. Image quality and visual perception.
Quality, quantity and geometry of an x-ray beam; effect on image quality. The primary X-ray image. Scatter grids and compensation filters. Appropriate exposure; timers and automatic exposure control, exposure indices, exposure factors and charts.
Digital image receptors; flat panel detectors and computed radiography. Basic construction, function, sensitivity and resolution. Image artefacts and the effects of image processing on image quality.
Students are required to participate in group work and practical exercises.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL311GEthicsMandatory (required) course2A mandatory (required) course for the programme2 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionThe course aims to strengthen students' independent thinking. We will discuss how best to discuss ethical problems and analyze ethical arguments. Common theories in ethics will also be discussed critically. Awareness of the principles underlying human relations and behaviours will be covered as well as the Code of Ethics for Radiologists.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL313GCPRMandatory (required) course1A mandatory (required) course for the programme1 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionFirst aid training.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL314GPharmacology and Contrast MediaMandatory (required) course5A mandatory (required) course for the programme5 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionHistory and development of CM.
Classification of CM.
Chemistry of CM.
Effects on CM on various body systems.
Indications and contraindication.
Patient risk groups and possible adverse reactions.
Acute and allergic reactions.
Pharmacology and drug effects.Face-to-face learningPrerequisites- Spring 2
GSL401GMRI Magnetic Resonance Imaging 1Mandatory (required) course6A mandatory (required) course for the programme6 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionThe structure and major components of magnetic resonance imaging equipment. Fundamental mathematics and physics of MRI. Magnetization of the body, the fundamentals of imaging and image reconstruction in MRI. MRI hardware and how individual components work. Overview of pulse sequences, rapid imaging, image quality and image artifacts. Pulse sequence for angiography and the use of contrast agents. Investigations of different parts of the body, patient preparation and patient care. Diseases seen in MRI. MRI safety.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesAttendance required in classGSL411GCT technology 1Mandatory (required) course4A mandatory (required) course for the programme4 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionBasic principles of computed tomography (CT), from x-ray beam attenuation to radiation detection, image reconstruction and display. The main factors affecting quality of CT examinations, in data acquisition as well as image reconstruction. Processing and visualization of images. CT examination procedures, contrast media, positioning and parameter selection.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL412GClinical Radiography 3Mandatory (required) course10A mandatory (required) course for the programme10 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionStudents are trained in radiographic positioning and procedures. Emphasis is placed on performing CT examinations, pediatric radiography and fluoroscopy.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesAttendance required in classGSL413GSectional anatomyMandatory (required) course2A mandatory (required) course for the programme2 ECTS, creditsCourse Description• Students are introduced to sectional anatomical plans - The appearance and characteristics of organs and organ systems in cross-section and other plans are discussed.
• Students are introduced to sectional anatomy and where they can look to review and gain more knowledge.
• The sectional anatomy will be reviewed as follows: sectional plans and review of bones, abdomen, thorax, spine, head and limbs.
• The course is mostly self-study with continuous assessment.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL414GFluoroscopyMandatory (required) course4A mandatory (required) course for the programme4 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionFluoroscopy and intervention: Equipment, techniques and radiation protection of patients and workers.
Equipment for measuring radiation dose and different methods for estimating effective dose.
Variation in effective doses and diagnostic reference levels.
Students are required to participate in group work and practical exercises.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL415GMedical imaging 3Mandatory (required) course4A mandatory (required) course for the programme4 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionIn all imaging departments, radiographers carry out medical imaging examinations and interventional procedures. It is important that radiologists, who carry out research, practice professional practices and show respect and devotion to their clients.
The aim of the course is to teach students to look at X-ray images while considering the correct projection, the most common abnormalities and the main diseases. Students are taught settings and how to see faults in projection and correct them.
Students learn about accident and emergency imaging performed outside of imaging departments. Students learn about the importance of professional and good communication with patients and colleagues.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisites- Fall
- GSL503GPediatric X-rayMandatory (required) course6A mandatory (required) course for the programme6 ECTS, creditsCourse Description
Pediatric imaging is an important part of the work of radiographers. In all imaging departments, children are part of the clients who come to the department and it is important that radiographers who perform imaging studies on children practice professional work practices and show children respect and care.
The aim of the course is to introduce students to pediatric imaging and the importance of good preparation for the radiographer when receiving children and their families.
The course will cover, among other things, the main pediatric diseases and injuries in children. The preparation, performance, lead protection and radiation protection of the main imaging studies will be reviewed. We will emphasize general X-ray studies but also introduce students to other imaging studies such as computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), ultrasound and isotopes.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL505GMagnetic Resonance Imagin 2Mandatory (required) course6A mandatory (required) course for the programme6 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionMRI course, part II: The aim of the course is to enhance the students knowledge of the basic physics of MRI introduced in part I of the MRI course (previous semester) and to associate the physics of MRI to clinical applications. The course consists of the following items:
- Pulse sequences and image contrast
- Tissue relaxation properties together with tissue proton density and appearance on images
- Historical developments in clinical MRI applications
- Examinations of organs and body-systems based on applications, indications, pathology and diagnosis. Includes central nervous system, muscular-skeletal system, thorax, heart and vasculature.
- Contrast agents in MRI: Types, indications for use and applications
- MRI safety
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL508GClinical Radiography 4Mandatory (required) course9A mandatory (required) course for the programme9 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionExecute general radiography examination. Emphasis is on training in angiography and MRI examination and procedures.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesAttendance required in classGSL509GNuclear medicine 1Mandatory (required) course4A mandatory (required) course for the programme4 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionRadioactivity, handling of radioactive material, examinations and imaging with gamma rays.
Radioactivity, alpha, beta and gamma radiation, decay and half-life.
An overview of production, transport, inventory and disposal of radioactive materials. Laws and regulations, with an emphasis on open radiation sources. Radionuclide generators, facilities, work practices and radiation protection. Handling, radiopharmacy and quality control of isotopes and carriers. Imaging with a gamma camera.
Diagnostic imaging with technetium, and other gamma-emitting substances, of the digestive system, urinary system, musculoskeletal system, respiratory system, endocrine system, cardiovascular system, and nervous system.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL510GScientific Research methodsMandatory (required) course5A mandatory (required) course for the programme5 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionThe course constitutes a practical guide to the preparation of a health-related research study. Modules include: reference search and handling, development of hypotheses, creation of a systematic critical review within chosen field of research, development and presentation of research proposals.
The course provide students knowledge of useful statistical methods appropriate for their project. The student also prepare and apply for a license according to their research.
The course is for graduate students who have chosen a field/research question for their dissertation project.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisites- Spring 2
GSL611GPathologyMandatory (required) course6A mandatory (required) course for the programme6 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionThis course aims for the student to gain an overview of the main diseases in the following categories: Cardiology, orthopedics (injuries and cold orthopedia), lung diseases, gastroenterology, neptrology, infectionous diseases, endocrine and metabolic diseases, brain and nervous diseases. Psychiatric and ear and throat. Normal appearance in X-ray, deviation, indications and contraindications. Diagnostic imaging.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL612GClinical radiography 5Mandatory (required) course5A mandatory (required) course for the programme5 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionClinical training in medical imaging department. Training in general radiographic examinations procedures. Emphasis is on nuclear medicine and MRI examinations.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesAttendance required in classGSL613GCT technology 2Mandatory (required) course4A mandatory (required) course for the programme4 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionClinical use of CT, indications and pathology in which CT examinations are most useful. Basic examinations of head, neck, spine, abdomen, and thorax. Radiation protection of patient and personnel related to CT examinations, radiation dose measurements and estimation of effective doses. Specific consideration for children and pregnant women.
The role of CT in nuclear medicine, CT angiographies and intervention.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL614LBS Project in RadiographyMandatory (required) course30A mandatory (required) course for the programme30 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionStudents select their own field of study in radiography and supply their knowledge in the field. Students work on a final paper according to their interest under supervision and present the results.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesPart of the total project/thesis creditsThird year- Fall
- GSL101GChemistryMandatory (required) course4A mandatory (required) course for the programme4 ECTS, creditsCourse Description
Basic principles of general chemistry, balancing equations, nomenclature, molar calculations, solubility, concentration. Basic principles of quantum chemistry, the atomic structure as a base for chemical properties and their reactions. Electron configuration and formation of chemical bonds. Basic introduction to theories of chemical bonding and molecular geometry and intermolecular forces. Basic principles of organic chemistry, nomenclature of organic compounds and functional groups. Organic polymers.
Teaching and learning activities:
Lectures, problem solving and homework.Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL102GIntroduction to medical imaging and analysisMandatory (required) course0A mandatory (required) course for the programme0 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionIntroduction to the history of medical imaging, from W.C. Röntgen's discoveries to modern technological advancements. The role, activities and obligations of Radiographers in the health care system. Field trips to Radiology Departments.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL103GRadiation Physics 1Mandatory (required) course4A mandatory (required) course for the programme4 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionIntroduction to radiation physics, radiation protection and medical imaging. Atoms, photons, electrons, magnetism and electromagnetic radiation, with a focus on x-rays. How x-rays are generated. Gamma radiation, radioactivity and half-life.
Lectures and home assignments based on material from the textbook.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL104GPhysicsMandatory (required) course2A mandatory (required) course for the programme2 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionStudents introduced to the basic applications of physics in health sciences. Example solutions to problems related to forces, motion, energy, etc., which will allow students to pursue further study and work in the health sciences.
Physics: Motion. Forces, Newton's law. Work, energy and power. Degree of heat, heat transport and thermodynamics. Hydrodynamics. Electrical forces and fields. Electricity, voltage and circuit. Magnetic field. Optics.
Lectures and electronic assignments based on the textbook material.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL105GMedical imaging 1Mandatory (required) course4A mandatory (required) course for the programme4 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionStudents receive instruction in the research technique used in performing general X-ray studies.
Students learn to view X-rays with respect to proper insertion, the most common variations and major diseases. The major tips and contraindications for X-ray studies will be discussed. The key concepts and word-of-speech radiologists will be discussed.
Students learn the importance of good communication.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesLEI102GAnatomyMandatory (required) course8A mandatory (required) course for the programme8 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionAnatomical methodology and descriptive terms. Terms of orientation with reference to the anatomical position. Fundamental principles of human body structure. Origins of the human body (embryology). Structure and function of the cell. Tissues.
Locomotor system. Nervous system. Cardiovascular system. Respiratory system. Lymphatic system. Digestive system. Urinary system. Endocrine system. Muscular system. Sensory systems. Reproductive system. Immune system. Hormonal system.Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesLEI107GCell biologyMandatory (required) course4A mandatory (required) course for the programme4 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionLectures: Topics, concepts and methods in biochemistry and cell biology. Genetic material, genome and genes, DNA replication and DNA metabolism. RNA, gene expression, transcription and protein translation. Proteins and enzymes. Metabolism of nucleotides, carbohydrates, lipids and amino acids. Nutrition, bioenergetics. Construction and properties of the cell membrane, membrane transport, cell organelles and intracellular transport, cell communication (signaling), the cytoskeleton, cell cycle, cell death and cell division.
Laboratory practicals: Pipettes og measuring techniques, spectrometry in enzymology, isolation of proteins and determination of protein concentration, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), enzyme kinetics.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesAttendance required in classLEI108GPhysiology 1Mandatory (required) course4A mandatory (required) course for the programme4 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionLectures: Homeostasis and control systems. Electrophysiology: membrane potentials and conduction. Endocrinology and nervous systems. Sensory physiology. Muscles: skeletal, smooth and cardiac muscles.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisites- Spring 2
GSL204GRadiation ProtectionMandatory (required) course4A mandatory (required) course for the programme4 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionThe use of radiation in the beginning of the century, radiation injuries. Methods of radiation detection and measurements. Biological effects of radiation on adults, children and foetus. Stochastic and non-stochastic effects of radiation. Carcinogenesis and hereditary effects. The International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP), justification, optimisation and limitation principles. Radiation protection of the workers and patients in diagnostic radiology. Acts and regulations concerning radiation protection. Background radiation, man-made radiation.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL206GRadiation Physics 2Mandatory (required) course4A mandatory (required) course for the programme4 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionEnergy spectrum of x-rays and attenuation in matter. Emphasis on how x-rays interact with matter, attenuation coefficients, half-value layers and factors that affect beam attenuation. Scatter radiation, radiation dose, and effective dose. Basic foundation of measurement of ionizing radiation and one practical exercise.
Lectures and a practical exercise related to the lecture material, which will require active participation from students.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL207GMedical imaging 2Mandatory (required) course3A mandatory (required) course for the programme3 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionStudents receive instruction in the research technique used in performing general X-ray studies of musculoskeletal, chest and abdominal.
Students learn to view X-rays with respect to proper insertion, the most common variations and major diseases of the musculoskeletal, breast and abdominal conditions. The major tips and contraindications for X-ray studies will be discussed. The key concepts and word-of-speech radiologists will be discussed.
Students learn the importance of good communication.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL208GClinical Radiography 1Mandatory (required) course5A mandatory (required) course for the programme5 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionThe students learn to perform the basics examinations of the skeleton and lungs.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesAttendance required in classGSL209GPatient careMandatory (required) course4A mandatory (required) course for the programme4 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionThe topic of this course is basic hospital operations and patient care.
Fundamental theories in nursing will be discussed. Students will get an introduction to hospital departments, the characteristics of different specialties, and the activities and roles of healthcare professions.
The course will cover patient admissions, reception, stays, treatment, discharge preparation, and preparation for examinations and operations. Also covered is patient care following operations, complications, and complication prevention.
Students will learn about caring for patients with neurological, metabolic, cardiopulmonary, urological, gastrointestinal, or joint diseases, as well as cancer care. Also nursing care of children and the specific needs of children.
The course will also discuss patient's safety needs and social needs, together with the care of family members. Confidentiality and patients' rights will be introduced, along with correct body posture and work techniques when caring for and transporting patients.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesLEI205GScience and data literacyMandatory (required) course6A mandatory (required) course for the programme6 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionThe course is divided into three parts: Presentation of scientific data, Literature search, and scientific and data literacy.
I. Presentation of scientific data
This section covers methodology for professional writing within the health sciences, as well as the structure and delivery of lectures. Database search and reference management software are also addressed. Students apply these methods in course assignments.
II. Literature search
Students receive instruction in the fundamentals of information searching.
III. Scientific and data literacy
An overview of statistics and the origin of data. Graphical representation of data and data distribution types. Confidence intervals. Sensitivity, specificity, and predictive values. An overview of study design and sampling as a representation of a population. Risk factors, risk, and relative risk. Interpretation of research results for an individual. Interpretation of research results in scientific papers and assessment of possible error sources.The course requires active participation. The material is covered in lectures, while methods are practiced in tutorial sessions and through assignments submitted orally and/or in writing.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesLEI206GPhysiology 2Mandatory (required) course4A mandatory (required) course for the programme4 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionLectures. Cardiovascular-, respiratory-, renal- and gastrointestinal physiology. Energy balance and control of metabolism and physiology of reproduction.
Practical lesson. Cardiovascular system. Participation is obligatory, lab report must be submitted, and online exam taken.
Project lessons. Twice during the course. Participation is obligatory
Partial exams. Three online partial exams will be applied. Students will be informed in more details at the beginning of the course.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesExtra material fee collectedHVS202GIntroduction to multidisciplinary health sciences - The health science dayMandatory (required) course1A mandatory (required) course for the programme1 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionThe course is especially aimed at students on their first year of studies in disciplines within the field of health sciences. The joint Health science day is for incoming students of all faculties at the School of Health Sciences in January each year. The main topic is interdisciplinary cooperation and its importance. All basic factors of cooperation will be covered such as the common view on the right to good health, communication and ethics. Furthermore, the role and responsibility of health sciences.
Distance learningPrerequisitesAttendance required in class- Fall
- GSL302GMicrobiology and infection controlMandatory (required) course4A mandatory (required) course for the programme4 ECTS, creditsCourse Description
The course consists of two main parts, microbiology and infection control. These parts are intergraded and provide the basis for knowledge and understanding of the characteristics of different pathogens and their relations to infectious diseases and the methods you can use for prevention of nosocomial or healthcare-associated infections.
Teaching/learning procedures:
In the teaching is based on lectures and includes following parts:- Microbiology – basics
- Microbiology – species/groups
- Bacterial infections in diverse organs and organ systems and major species in healthcare associated infections.
- Infection control
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL307GVascular ultrasoundMandatory (required) course4A mandatory (required) course for the programme4 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionThis course will cover the basics of ultrasound imaging such as physics of sound waves, properties of reflection from major tissues and main processing methods and their use. Also, the functionality of the ultrasound equipment will be introduced in detail along with discussion of the importance of image quality, its improvement and impact factors.
Carotid artery is the main subject with introduction to cardiovascular ultrasound. The anatomy of the carotid artery along with the surrounding tissues and their appearance in ultrasound images will be described. Students learn to recognize and identify the normal appearance of the carotid artery in ultrasound images and also identify and recognize common abnormalities and major manifestations. Students are given tasks where they perform ultrasound imaging of the common carotid artery and process their results.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL309GClinical Radiography 2Mandatory (required) course8A mandatory (required) course for the programme8 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionStudents receive training in performing general X-ray examinations. Receive training in contrast material handling and needle placement. Receive training in performing simple CT scans.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesAttendance required in classGSL310GRadiographic EquipmentMandatory (required) course6A mandatory (required) course for the programme6 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionGeneral introduction of common radiographic equipment and short overview of the history of radiographic imaging. Introduction of equipment for mammography, tomography, dental radiography and veterinary use.
Basic properties of digital images. Pixels, their size and depth; monochrome and color images, greyscale and different color models. Image file formats and compression. Contrast- and spatial resolution. Fundamentals of digital image processing: look-up-tables and spatial filtering. Image quality and visual perception.
Quality, quantity and geometry of an x-ray beam; effect on image quality. The primary X-ray image. Scatter grids and compensation filters. Appropriate exposure; timers and automatic exposure control, exposure indices, exposure factors and charts.
Digital image receptors; flat panel detectors and computed radiography. Basic construction, function, sensitivity and resolution. Image artefacts and the effects of image processing on image quality.
Students are required to participate in group work and practical exercises.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL311GEthicsMandatory (required) course2A mandatory (required) course for the programme2 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionThe course aims to strengthen students' independent thinking. We will discuss how best to discuss ethical problems and analyze ethical arguments. Common theories in ethics will also be discussed critically. Awareness of the principles underlying human relations and behaviours will be covered as well as the Code of Ethics for Radiologists.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL313GCPRMandatory (required) course1A mandatory (required) course for the programme1 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionFirst aid training.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL314GPharmacology and Contrast MediaMandatory (required) course5A mandatory (required) course for the programme5 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionHistory and development of CM.
Classification of CM.
Chemistry of CM.
Effects on CM on various body systems.
Indications and contraindication.
Patient risk groups and possible adverse reactions.
Acute and allergic reactions.
Pharmacology and drug effects.Face-to-face learningPrerequisites- Spring 2
GSL401GMRI Magnetic Resonance Imaging 1Mandatory (required) course6A mandatory (required) course for the programme6 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionThe structure and major components of magnetic resonance imaging equipment. Fundamental mathematics and physics of MRI. Magnetization of the body, the fundamentals of imaging and image reconstruction in MRI. MRI hardware and how individual components work. Overview of pulse sequences, rapid imaging, image quality and image artifacts. Pulse sequence for angiography and the use of contrast agents. Investigations of different parts of the body, patient preparation and patient care. Diseases seen in MRI. MRI safety.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesAttendance required in classGSL411GCT technology 1Mandatory (required) course4A mandatory (required) course for the programme4 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionBasic principles of computed tomography (CT), from x-ray beam attenuation to radiation detection, image reconstruction and display. The main factors affecting quality of CT examinations, in data acquisition as well as image reconstruction. Processing and visualization of images. CT examination procedures, contrast media, positioning and parameter selection.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL412GClinical Radiography 3Mandatory (required) course10A mandatory (required) course for the programme10 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionStudents are trained in radiographic positioning and procedures. Emphasis is placed on performing CT examinations, pediatric radiography and fluoroscopy.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesAttendance required in classGSL413GSectional anatomyMandatory (required) course2A mandatory (required) course for the programme2 ECTS, creditsCourse Description• Students are introduced to sectional anatomical plans - The appearance and characteristics of organs and organ systems in cross-section and other plans are discussed.
• Students are introduced to sectional anatomy and where they can look to review and gain more knowledge.
• The sectional anatomy will be reviewed as follows: sectional plans and review of bones, abdomen, thorax, spine, head and limbs.
• The course is mostly self-study with continuous assessment.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL414GFluoroscopyMandatory (required) course4A mandatory (required) course for the programme4 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionFluoroscopy and intervention: Equipment, techniques and radiation protection of patients and workers.
Equipment for measuring radiation dose and different methods for estimating effective dose.
Variation in effective doses and diagnostic reference levels.
Students are required to participate in group work and practical exercises.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL415GMedical imaging 3Mandatory (required) course4A mandatory (required) course for the programme4 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionIn all imaging departments, radiographers carry out medical imaging examinations and interventional procedures. It is important that radiologists, who carry out research, practice professional practices and show respect and devotion to their clients.
The aim of the course is to teach students to look at X-ray images while considering the correct projection, the most common abnormalities and the main diseases. Students are taught settings and how to see faults in projection and correct them.
Students learn about accident and emergency imaging performed outside of imaging departments. Students learn about the importance of professional and good communication with patients and colleagues.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisites- Fall
- GSL503GPediatric X-rayMandatory (required) course6A mandatory (required) course for the programme6 ECTS, creditsCourse Description
Pediatric imaging is an important part of the work of radiographers. In all imaging departments, children are part of the clients who come to the department and it is important that radiographers who perform imaging studies on children practice professional work practices and show children respect and care.
The aim of the course is to introduce students to pediatric imaging and the importance of good preparation for the radiographer when receiving children and their families.
The course will cover, among other things, the main pediatric diseases and injuries in children. The preparation, performance, lead protection and radiation protection of the main imaging studies will be reviewed. We will emphasize general X-ray studies but also introduce students to other imaging studies such as computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), ultrasound and isotopes.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL505GMagnetic Resonance Imagin 2Mandatory (required) course6A mandatory (required) course for the programme6 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionMRI course, part II: The aim of the course is to enhance the students knowledge of the basic physics of MRI introduced in part I of the MRI course (previous semester) and to associate the physics of MRI to clinical applications. The course consists of the following items:
- Pulse sequences and image contrast
- Tissue relaxation properties together with tissue proton density and appearance on images
- Historical developments in clinical MRI applications
- Examinations of organs and body-systems based on applications, indications, pathology and diagnosis. Includes central nervous system, muscular-skeletal system, thorax, heart and vasculature.
- Contrast agents in MRI: Types, indications for use and applications
- MRI safety
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL508GClinical Radiography 4Mandatory (required) course9A mandatory (required) course for the programme9 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionExecute general radiography examination. Emphasis is on training in angiography and MRI examination and procedures.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesAttendance required in classGSL509GNuclear medicine 1Mandatory (required) course4A mandatory (required) course for the programme4 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionRadioactivity, handling of radioactive material, examinations and imaging with gamma rays.
Radioactivity, alpha, beta and gamma radiation, decay and half-life.
An overview of production, transport, inventory and disposal of radioactive materials. Laws and regulations, with an emphasis on open radiation sources. Radionuclide generators, facilities, work practices and radiation protection. Handling, radiopharmacy and quality control of isotopes and carriers. Imaging with a gamma camera.
Diagnostic imaging with technetium, and other gamma-emitting substances, of the digestive system, urinary system, musculoskeletal system, respiratory system, endocrine system, cardiovascular system, and nervous system.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL510GScientific Research methodsMandatory (required) course5A mandatory (required) course for the programme5 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionThe course constitutes a practical guide to the preparation of a health-related research study. Modules include: reference search and handling, development of hypotheses, creation of a systematic critical review within chosen field of research, development and presentation of research proposals.
The course provide students knowledge of useful statistical methods appropriate for their project. The student also prepare and apply for a license according to their research.
The course is for graduate students who have chosen a field/research question for their dissertation project.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisites- Spring 2
GSL611GPathologyMandatory (required) course6A mandatory (required) course for the programme6 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionThis course aims for the student to gain an overview of the main diseases in the following categories: Cardiology, orthopedics (injuries and cold orthopedia), lung diseases, gastroenterology, neptrology, infectionous diseases, endocrine and metabolic diseases, brain and nervous diseases. Psychiatric and ear and throat. Normal appearance in X-ray, deviation, indications and contraindications. Diagnostic imaging.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL612GClinical radiography 5Mandatory (required) course5A mandatory (required) course for the programme5 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionClinical training in medical imaging department. Training in general radiographic examinations procedures. Emphasis is on nuclear medicine and MRI examinations.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesAttendance required in classGSL613GCT technology 2Mandatory (required) course4A mandatory (required) course for the programme4 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionClinical use of CT, indications and pathology in which CT examinations are most useful. Basic examinations of head, neck, spine, abdomen, and thorax. Radiation protection of patient and personnel related to CT examinations, radiation dose measurements and estimation of effective doses. Specific consideration for children and pregnant women.
The role of CT in nuclear medicine, CT angiographies and intervention.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesGSL614LBS Project in RadiographyMandatory (required) course30A mandatory (required) course for the programme30 ECTS, creditsCourse DescriptionStudents select their own field of study in radiography and supply their knowledge in the field. Students work on a final paper according to their interest under supervision and present the results.
Face-to-face learningPrerequisitesPart of the total project/thesis credits
Additional information The University of Iceland collaborates with over 400 universities worldwide. This provides a unique opportunity to pursue part of your studies at an international university thus gaining added experience and fresh insight into your field of study.
Students generally have the opportunity to join an exchange programme, internship, or summer courses. However, exchanges are always subject to faculty approval.
Students have the opportunity to have courses evaluated as part of their studies at the University of Iceland, so their stay does not have to affect the duration of their studies.
The work of a radiographer is interesting and varied. The profession is expanding year on year, since methods for looking inside the human body are under continuous development.
Modern radiographers use X-rays, magnetic fields, radio waves, radioactive materials, sound waves and computer technology to examine everything from the surface of large organs to the workings of cells.
This programme could open up careers in:
- Imaging analysis departments
- Healthcare institutions
- Private companies
- Icelandic Cancer Society
- Radiotherapy departments
- Icelandic Radiation Safety Authority
- University of Iceland
- Icelandic Heart Association
This list is not exhaustive.
- The organisation for students in radiography and biomedical science is called FLOG.
- FLOG organises events such as socials for new students, annual galas and workplace tours
- FLOG on Facebook
Students' comments  I struggled to decide on my future career path but ultimately chose radiography, and I have no regrets. Radiographers work not only with advanced equipment but closely with other healthcare professionals and patients. The programme is demanding yet highly rewarding.
I struggled to decide on my future career path but ultimately chose radiography, and I have no regrets. Radiographers work not only with advanced equipment but closely with other healthcare professionals and patients. The programme is demanding yet highly rewarding. Although I knew little about the field initially, I was continually surprised and thrilled with my choice. The programme is varied and exciting, with extensive practical training. Radiology is a fundamental part of healthcare, and it's wonderful to be part of it.
Although I knew little about the field initially, I was continually surprised and thrilled with my choice. The programme is varied and exciting, with extensive practical training. Radiology is a fundamental part of healthcare, and it's wonderful to be part of it.Helpful content Study wheel
What interests you?
How to apply
Follow the path
Contact us If you still have questions, feel free to contact us.
Radiography & Biomedical ScienceWeekdays 9 am - 12 pm.Social media
Share